Active Directory Domain Services is a directory service which provide centralized authentication to computers and users. For ADDS I think no introduction is required, because it is used by small to large scale organizations for many number of years. Most of the organizations implement ADDS but does not follow Microsoft security best practices to maintain the AD infrastructure. This is a critical system, if an intruder gain access to ADDS, they can gain access to any other system which depend on ADDS.
Microsoft has released a white paper “Best Practices for Securing Active Directory”, which describe all the security aspects to protect ADDS. But it’s kind of a long term adaptation. So I have decided to write some important tasks you can follow and implement to enable security best practices and add additional layer of protection to your Active directory infrastructure.
- Domain controller Naming convention
Domain controllers should not be named as DC01, HODC, PRDC01, or something which says it’s a domain controller. If DC’s were easy to identify, intruder have more time to attack it. So always use some different naming convention to servers. This practice is good to follow on all other application servers and services.
- Software patching and use of up-to-date Operating systems for Domain controllers and Clients
Administrators ignore to install patches for domain controllers because of the fear of something might go wrong. But Microsoft release these software updates to address vulnerabilities. At least security updates should be installed on time. If you sees a risk, install updates on an additional domain controller and let it run for few days, then updates the primary DC.
Windows server 2012 R2 Active directory domain services is the latest version. Upgrading to it will give you more enhanced features and capabilities. If you have windows XP and windows server 2003 please upgrade them right away. Because these OS’s are not supported. Running unsupported versions are high risk to the IT environment.
- Securing Local Administrator Accounts on Workstations and Member Servers
Most of the organizations Installation of Operating system is done by IT support desk or some outsourced company. So they will know the local administrator account details. This can be considered as a risk because any time they can login to these computers to copy data and install some software’s.
Using active directory group policy this can be centrally managed. We can disable the administrator account, rename, set different password or create a new local account. For my practice, I always disable the local administrator account and create a new account which is belong to the local administrators group.
a. Navigate to the Group Policy management
b. Create new GPO
c. Edit GPO, Computer Configuration – Preferences – Control Panel Settings – Local users and groups
d. To Disable the Administrator account
i. Select new Local User, User name – Administrator (built in), tick – Account disabled, Action - Update

e. Create a new Local account
i. Select new Local User, User name – PCUser (type the desired account name), tick – Password never expire, tick- user cannot change password, tick- account never expire, Action – Create

f. Add created account to the local administrator group
i. Select new Local Group, Group name – Administrators, Action - Update
ii. Add – Type the previously created user name
Remember you cannot browse for accounts, you have to type the exact account name.

According to the Microsoft security best practices domain administrator account should be disabled. But most organizations don’t follow these steps because they used to perform certain operations using this built in administrator account. So it’s important to follow these practices.
· Rename Administrator account
· Use Strong Password
· If possible, Use smart card or multi-factor-authentication.

Windows firewall should be enabled in all domain controllers. Also if you have an internal firewall use it in domain controller and client network, use following firewall exceptions
https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd772723(v=ws.10).aspx
- Delegate administrative tasks to different accounts.
Administrative tasks should be identified and delegated permissions only to perform those operations. In example there are IT help desk staff only perform unlock accounts and reset passwords. These staff only require permission to perform those tasks.
Following is how to enable delegation to two common operations,
a. Enable delegation to Add computers to Domain
i. Navigate to active directory users and computers
ii. Select the desired OU, All tasks, Delegate control and select the user account
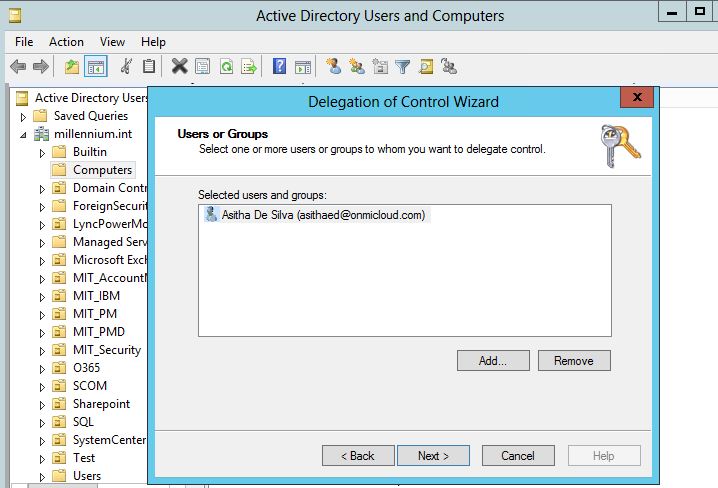
iii. Create custom task
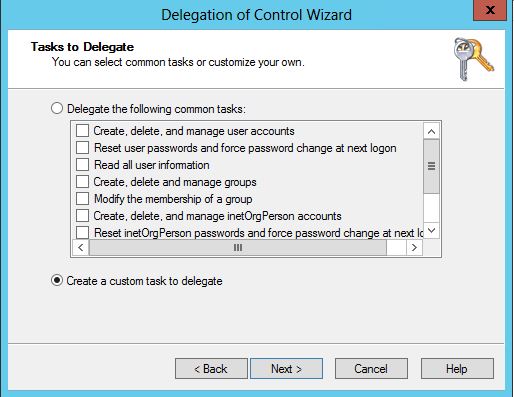
iv. Add following information
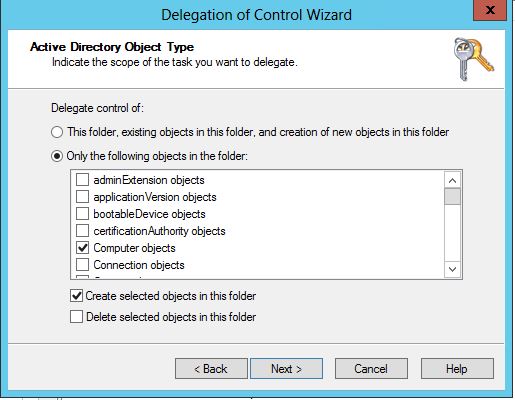
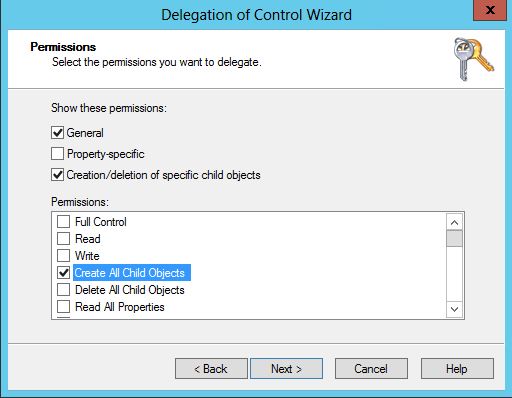
v. Complete the delegation
b. Delegate password reset and enable disable rights to user account
i. In the delegation wizard add following permissions to enable password reset
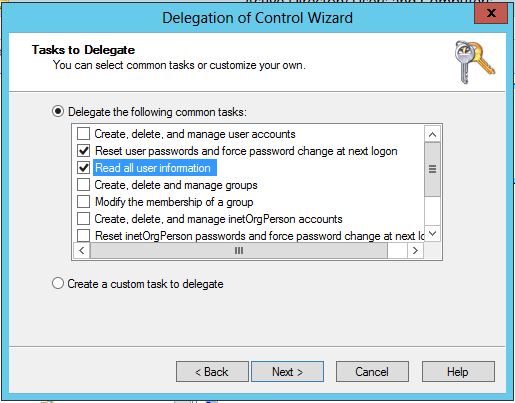
ii. Add enable disable user accounts permissions
1. Select create a custom task to delegate
2. Select user object
3. Select the 'General’, 'Property-specific' checkboxes and Select ‘Read userAccountControl’, ‘Write userAccountControl’, ‘Change password’, ‘Reset password’
- Maintain separate administrator accounts
IT Administrators should not be logging to their PC’s using admin privileged accounts. If there are malware or harmful application installed in PC’s, it can use the login privileges and propagate to other systems to do the damage. So administrators have to use normal domain user accounts to login their computers and keep their admin account separately.
Audit policies are really important when tracking changes to the system. But it should planned carefully. Because when all the events are logged, log files grow massive in size. For domain controller GPO I’m recommending to enable following audit polices.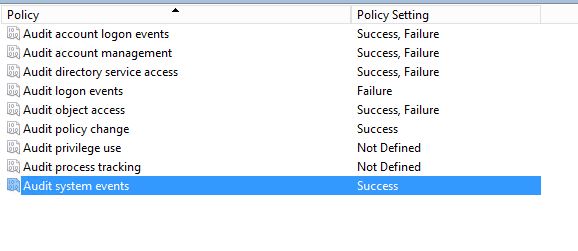
- Limit physical access to Domain controllers.
Physical security is a very important point of consideration for Domain controllers, there are scenarios that active directory infrastructure is extended to branches and additional domain controllers are placed in these remote locations. In these scenarios make sure to place the domain controller in a secure location which is access only authorized to IT staff. Also if you cannot guarantee the access, just place a read only domain controller.
In windows server 2008R2 there are ways to crack the administrator password using installation DVD and selecting repair mode. We will discuss is from another post J, so secure access to the server.
This post only cover few basic security practices which you can implement easily in your organization, but if you wish to implement more secure environment, I’m recommending you to read and follow the Microsoft security best practice guide for active directory.
https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dn487446.aspx
Hope this post is helpful
cheers
Asitha De Silva (https://lk.linkedin.com/pub/asitha-de-silva/27/b09/429)




