
AI has great potential to maximize the value of data. However, it's important to understand that the effectiveness of AI is directly dependent on the quality of the underlying data. AI requires a robust analytic platform that can manage and govern data across an entire organization, including data from various sources such as enterprise systems, Cloud services, and partner networks. To address this need, Oracle has developed an Autonomous Database within Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI). This solution is a comprehensive, modern data analytics platform integrated into a single Cloud service.
Autonomous Database: Modern Data Analytics Platform
The process begins with data. Data can be sourced from object stores, other Clouds, SaaS applications, on-premises database applications, and streaming sources, all integrated into Oracle Database 23ai. This is a converged database platform, capable of managing data while providing a broad range of analytics. Autonomous Database is much more than a traditional database; it serves as a complete ecosystem for data analytics. The converged database is designed to support multiple personas. Data analysts allow access to data modeling and visualization tools, while developers benefit from a low-code application development environment for quickly building analytic applications. Data scientists can use an end-to-end machine learning environment, and data engineers are equipped with powerful transformation tools. All these capabilities are natively built into an Autonomous Database, eliminating the need to integrate into other Cloud services or products.
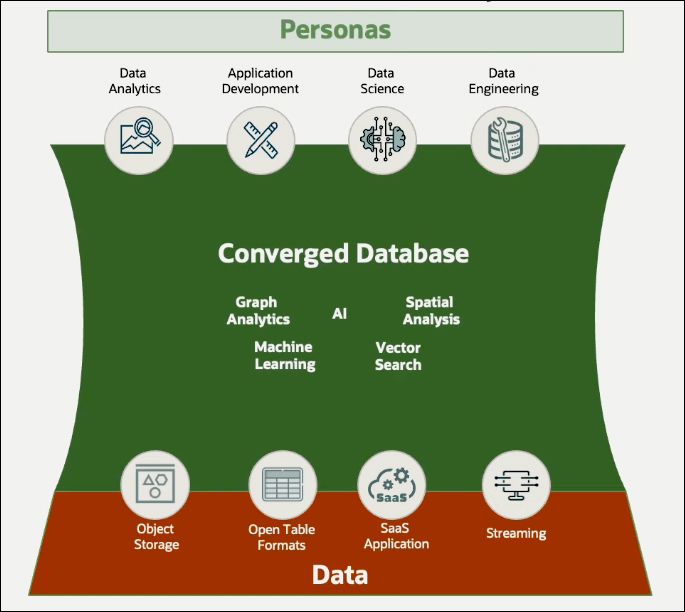
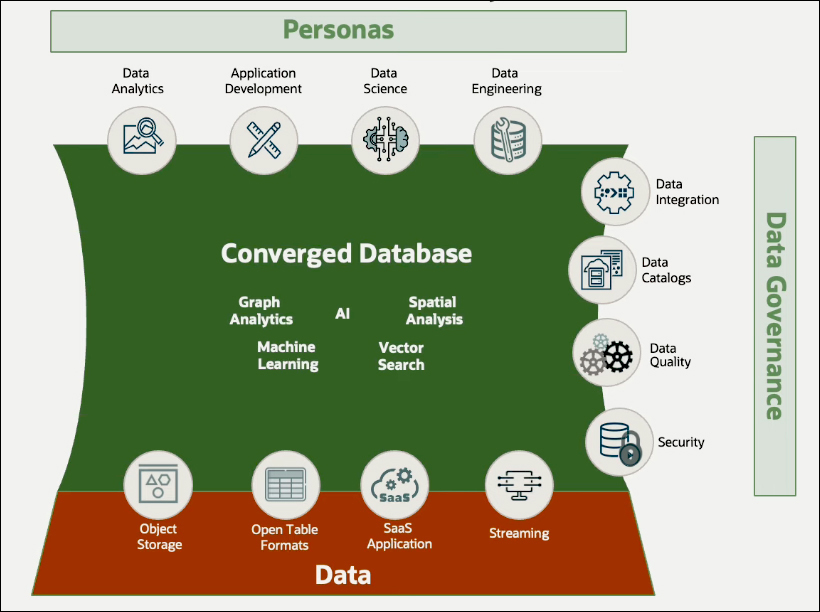
Data is managed within a database, supported by tools and experiences tailored for different personas. Capabilities for data governance, including cost governance features, are also provided. A data catalog gives users visibility into all data, not just within their database but throughout the accessible Cloud environments. Advanced data security capabilities are also implemented to ensure compliance with necessary privacy policies.
A modern analytics platform is not an isolated system. It's part of a broader data ecosystem. It is essential for seamless data exchange between different platforms. To support this, data sharing capabilities and the data marketplace are available.
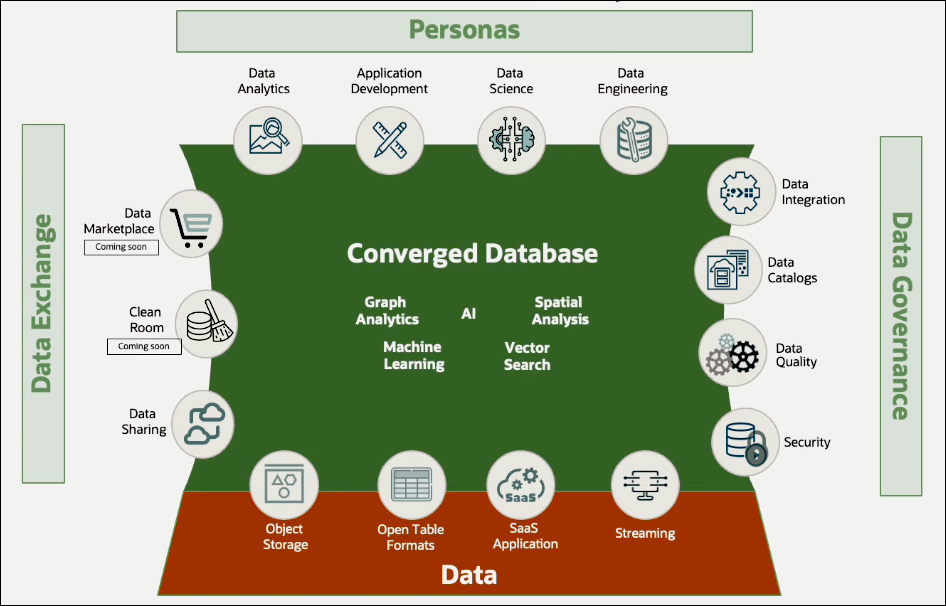
Autonomous Database and the Data Ecosystem
Many are already familiar with Oracle Database. However, the key difference between it and Autonomous Database is its simplicity in accessing data from anywhere in the Cloud.
Data Lake File Formats: Object storage allows access to data lake files, including Parquet, Iceberg tables, Avro, JSON, and CSV. Users can load these files into their database or query them directly in a data lake style without moving the data from its original location.
Secure Object Store Access: Data can be accessed securely from any Cloud environment, whether in Oracle OCI, AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud. This secure access is enabled through native Cloud authentication methods. Communication between the database and the object store is encrypted, ensuring that access remains highly secure even when querying data across multiple Clouds.
Data Catalogs: Integration with data catalogs is essential to understand the data stored in other Clouds. Oracle offers integration with AWS Glue, allowing users to discover and access data across different Cloud environments.
Data Virtualization: While accessing data in object storage is important, not all data resides in files or object stores. To address this, Autonomous Database offers data virtualization or federation capabilities, enabling direct connections to non-Oracle databases
Data Integration: Traditional ETL processes are supported, with Autonomous Database offering connections to over 100 data sources.
Data Streaming: Integration with Kafka and other streaming environments is straightforward, allowing easy data ingestion into an Autonomous Database.
How does Autonomous Database simplify data access across all Clouds?
Autonomous Database provides secure access to data in AWS, Azure, and GCP by integrating with their native access control mechanisms, such as AWS Resource Names. This allows Autonomous Database to securely read data stored in your AWS data lake. The communication is encrypted, ensuring the security of the entire data transfer process. Different file types are supported in object storage, as Autonomous Database supports standard formats, including Parquet, Avro, ORC, CSV, and JSON. Also, it supports open table formats, enabling access to Apache Iceberg tables and Delta Share tables. This capability allows interaction with all Cloud data.
Accessing data from other databases, including non-Oracle ones, is just as simple. Autonomous Database includes built-in capabilities to access various data stores. For example, you can execute SQL queries against Azure SQL, Amazon Redshift, MySQL, or Snowflake. Suppose you have privileges to access a Redshift database. In that case, you can set up a link in the Autonomous Database and directly run an SQL query to retrieve data from that Redshift database.
Personas
The modern data analytics platform with Autonomous Database supports a wide range of analytics users, enabling them to work with their data.
For Data Engineers: Autonomous Database includes a fully managed data integration solution that is integrated directly into the platform, and there is no need for a separate tool. The transformation capabilities offer a range of options and provide a drag-and-drop interface for creating data flows, allowing users to transform raw data into the desired format. This functionality is fully built into the Autonomous Database, requiring no additional installation or management.
For Data Scientists: Autonomous Database offers an end-to-end machine learning and data science platform. It includes scalable machine learning algorithms integrated directly into the database, along with a user-friendly notebook environment. Data scientists can work in a familiar interface, using Python or R instead of SQL to build their machine-learning models. For those who like assistance, built-in AutoML capabilities and a user interface are available to accelerate the development of new models and help select the right algorithms for specific business challenges. The platform is enterprise-ready, providing end-to-end model management to support the deployment of models into production and ensuring ongoing monitoring and maintenance to maintain accuracy over time.
For Application Developers: Autonomous Database offers a powerful low-code environment called APEX, enabling rapid development of new applications directly on the database. These applications can be accessed via web or mobile platforms. While the modern data analytics platform may seem focused only on analytics, it also supports numerous use cases for building simple applications that can be quickly deployed to a large number of users.
For Data Analysts: Autonomous Database offers an end-to-end experience with Data Studio and provides tools for data analysts who may not write their own SQL but want to interact with the data. Built into Autonomous Database, these capabilities include access to a data catalog for exploring available data, simple loading and transformation of that data, analysis and visualization features, and options for sharing insights.
For Everyone: One of the key features introduced is the integration of large language models into the Autonomous Database, called Select AI. This functionality allows users to ask natural language questions directly to the database. It is accessible from any Oracle tool or environment that can connect to a database. This is not a standalone chatbot. It is a core technology embedded within the database that is accessible to all Oracle database applications.
Data Governance
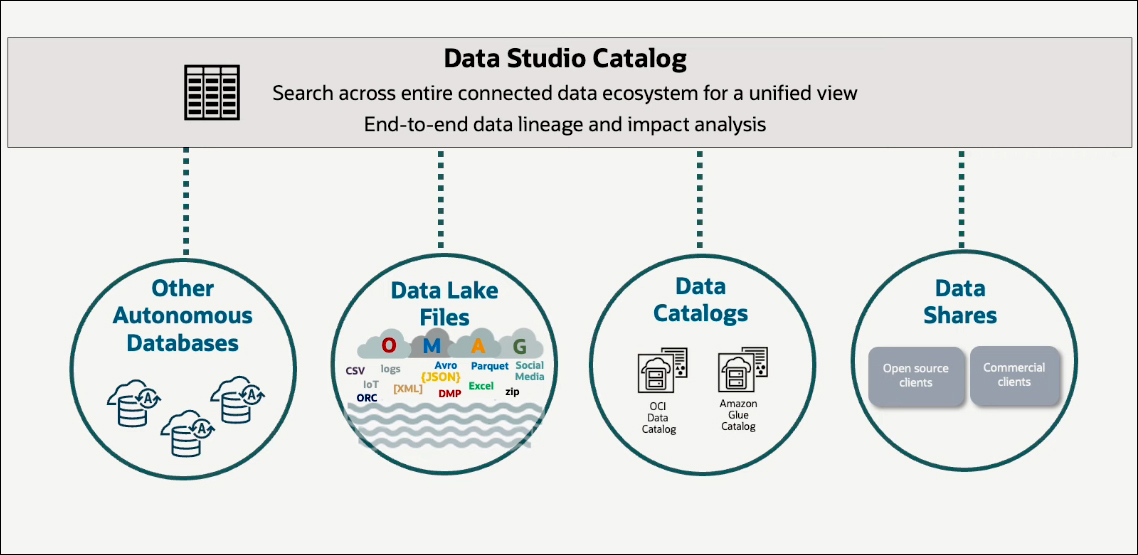
It begins with understanding what data is available. In Autonomous Database, the Data Studio catalog serves as a centralized location where users can view all accessible data from their database and other Autonomous Databases, object storage, data lake files, and external data catalogs or data shares. This data catalog offers a comprehensive overview of the entire data ecosystem that can be accessed, queried, and processed with an Autonomous Database. It provides critical information about the data, including lineage, which indicates the source of the data. This helps users understand what data is available and which can be used.
Another critical aspect of governance is security. Autonomous Database features a robust security capability called Data Safe, which ensures data protection. While every database allows access control privileges for specific tables or objects, Data Safe goes beyond that. It assesses users and their granted privileges, determining whether they are appropriate. Also, Data Safe analyzes the database to identify potentially sensitive data, providing alerts and helping in data masking within applications. This capability addresses complex data governance challenges by helping to understand the nuances of data and applications while ensuring that appropriate security policies are enforced.
Data Exchange
A significant area of investment has been in data exchange, particularly in data sharing capabilities within autonomous databases. Oracle provides two types of data sharing for users. The open-source Delta Sharing protocol enables sharing of data from an Autonomous Database with non-Oracle users. For example, if a user wants to share datasets with someone using Microsoft Power BI, they can do so through Delta Sharing. The user specifies the dataset they wish to share and notifies the recipient about the shared dataset, and the recipient can then securely access it. Delta Sharing is compatible with a wide range of open-source frameworks, business analytics tools, and other databases.
Oracle enables efficient data sharing between Oracle Autonomous Databases through optimized Oracle Cloud links. This allows one Autonomous Database to link and share data with another Autonomous Database. Also, using the Delta Sharing protocol, the Autonomous Database can ingest data from external sources. For example, if you have a Databricks system, data shared from Databricks can be accessed by Autonomous Database and vice versa, allowing data to be shared back to Databricks.
The upcoming Data Marketplace feature within Autonomous Database is a simple application of data sharing. Users will be able to access the Data Marketplace application, browse available datasets, and select specific datasets of interest. For example, a user might choose to view marketing leads from a recent event, examine the data, and then load it into their database for analysis. This capability offers a simple and efficient way to share data across the organization, maximizing the value of data within Oracle-based enterprise databases.
Reference:
Oracle DatabaseWorld AI Edition





